Introduction
Hair loss, or alopecia, is a widespread condition affecting millions globally, irrespective of gender or age. It can manifest in various forms, from temporary shedding to permanent hair loss, significantly impacting an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life. This article explores the different types of hair loss, their underlying causes, and the most effective hair loss treatment strategies available today.

Understanding Hair Loss
Hair loss is broadly classified into two main categories:
- Non-scarring alopecia: This type of hair loss is often reversible and characterized by the miniaturisation of hair follicles or disruption of the hair growth cycle. Common examples include androgenetic alopecia (AGA), alopecia areata (AA), and telogen effluvium (TE).
- Scarring alopecia: Also known as cicatricial alopecia, this condition involves irreversible damage and destruction of hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss. It is often caused by inflammatory or autoimmune processes. Examples include lichen planopilaris (LPP), discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA).
Non-Scarring Alopecia: Causes and Treatment
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)
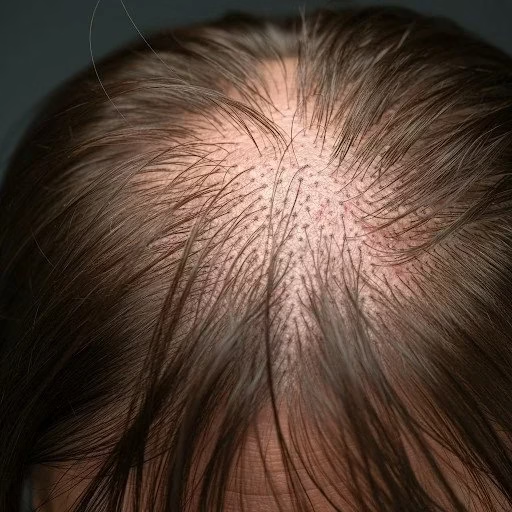
AGA, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, is the most prevalent form of hair loss. It is driven by genetic predisposition and hormonal factors, primarily the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Hair Loss Treatment:
- Minoxidil: A topical solution that promotes hair growth by prolonging the hair cycle’s anagen (growth) phase and increasing blood flow to the scalp. Available over-the-counter in 2% and 5% concentrations, it is effective for both men and women.
- Finasteride: An oral medication that inhibits the conversion of testosterone to DHT. It is FDA-approved for men and has shown significant efficacy in slowing down hair loss and promoting regrowth.
- Hair Transplantation: A surgical procedure that involves harvesting hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back of the head) and transplanting them to the balding areas. It offers a permanent solution for hair loss but can be costly.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Devices that emit low-level laser light to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. While evidence supporting its efficacy is still emerging, it is often used as an adjunctive therapy.
2. Alopecia Areata (AA)
AA is an autoimmune disorder that causes patchy hair loss on the scalp, face, and other parts of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles.
Hair Loss Treatment:
- Corticosteroids: Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that can be administered topically, intralesionally (injected into the affected areas), or systemically (oral or intravenous). They help suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors: A newer class of drugs that block the JAK-STAT pathway, which plays a crucial role in the immune response. JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib and ruxolitinib have shown promising results in treating AA.
- Immunotherapy: Topical immunotherapy involves applying chemicals like diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP) to the scalp to induce an allergic reaction, which can stimulate hair regrowth.
- Anthralin: A topical medication that alters the immune response and promotes hair growth. It can be messy and may cause skin irritation.
3. Telogen Effluvium (TE)
TE is a common type of hair loss triggered by stress, illness, hormonal changes, or medications. It is characterized by a sudden increase in shedding, resulting in diffuse hair thinning.
Hair Loss Treatment:
- Addressing the underlying cause: Identifying and managing the trigger factor is crucial for resolving TE.
- Minoxidil: Can be helpful in promoting hair regrowth during the recovery phase.
- Nutritional Support: Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly iron and zinc, is important for hair health.
Scarring Alopecia: Causes and Treatment
Scarring alopecia is a group of conditions that cause permanent hair loss due to inflammation and destruction of hair follicles. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further hair loss and manage associated symptoms.
Common Types:
- Lichen Planopilaris (LPP): An inflammatory condition that primarily affects the scalp, causing itching, burning, and permanent hair loss.
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE): A chronic autoimmune disease that can affect the skin and scalp, leading to scarring and hair loss.
- Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA): A type of scarring alopecia that predominantly affects women of African descent, starting at the crown of the head and progressing outwards.
Hair Loss Treatment:
- Corticosteroids: Topical, intralesional, or systemic corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response.
- Hydroxychloroquine: An antimalarial drug with anti-inflammatory properties, commonly used in treating DLE.
- Retinoids: Oral medications derived from vitamin A that can help regulate skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like methotrexate or mycophenolate mofetil may be used in severe cases to suppress the immune system.
- Biologics: A newer class of drugs that target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process.
Emerging Therapies
Research in hair loss treatment is ongoing, with promising new therapies on the horizon:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Utilising stem cells to regenerate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
- Gene Therapy: Targeting the genes responsible for hair loss to correct the underlying genetic defects.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
In addition to medical hair loss treatment and surgical treatments, several non-pharmacological approaches can complement hair loss treatment:
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): A cosmetic tattooing technique that creates the appearance of hair follicles on the scalp, providing the illusion of fuller hair.
- Wigs and Hairpieces: A non-surgical option for concealing hair loss and restoring confidence.
- Camouflage Products: Powders, sprays, and lotions that can be used to conceal thinning hair and create the appearance of greater density.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress management techniques, a balanced diet, and proper hair care practices can improve overall hair health.
Psychological Impact and Support
Hair loss can have a profound psychological impact, leading to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. It is crucial to address these emotional aspects alongside hair loss treatment. Support groups, counselling, and psychotherapy can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges associated with hair loss.
Conclusion
Hair loss is a complex condition with diverse causes and manifestations. Effective management requires a comprehensive approach that considers individual needs and preferences. A thorough evaluation by a hair loss treatment specialist is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalised treatment planning. With advancements in medical and surgical interventions, coupled with supportive care, individuals experiencing hair loss can significantly improve their hair growth and overall quality of life.