Rosacea
Understanding Rosacea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
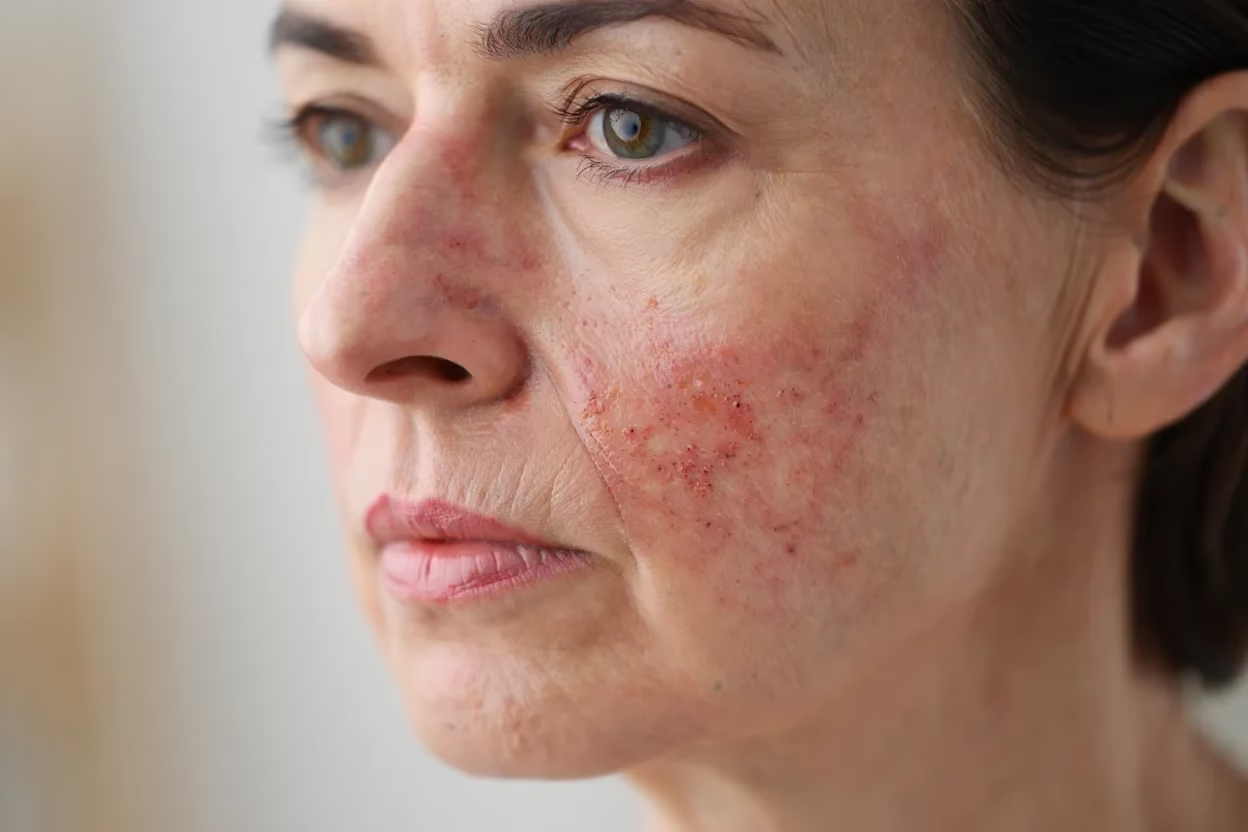
This chronic skin condition can cause redness, flushing, and sometimes bumps or pimples. Our approach involves calming inflammation, reducing redness, and managing breakouts with a combination of medical-grade skincare and tailored treatments.
Rosacea Treatment Options
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the central areas of the face. Symptoms include facial redness, visible blood vessels, bumps, pimples, and, in severe cases, skin thickening. Although there is no cure for rosacea, many treatments can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Assessment
Rosacea varies in each individual, so proper assessment is essential for effective treatment. Symptoms can range from persistent redness and flushing to thickened skin (phymatous changes), papules, pustules, and even eye involvement. A healthcare professional will assess the severity of symptoms and recommend the best treatment plan.
Lifestyle and Skincare Adjustments
- Avoiding Triggers: Common triggers include sun exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress. Identifying and avoiding these can help reduce flare-ups.
- Gentle Skincare: Use mild cleansers and avoid harsh scrubbing. Regular moisturising with emollients helps maintain the skin’s barrier function.
- Sun Protection: Daily broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher helps prevent flare-ups and slows disease progression.
- Cosmetic Camouflage: Green-tinted foundations and powders can conceal redness and visible blood vessels, improving appearance.
Treatment Approach
First-Line Interventions
Behavioural Changes: Focus on avoiding triggers, sun protection, and gentle skincare.
Second-Line Interventions
If lifestyle adjustments are insufficient, medical treatments like laser therapy, intense pulsed light (IPL), or medication may be necessary.
Pharmacological Therapy
Topical Treatments
- Brimonidine: Constricts blood vessels, reducing facial redness. It is applied once daily, and results are visible within hours.
- Oxymetazoline: Similar to brimonidine, this reduces redness for up to 12 hours and is applied once daily.
Papules and Pustules
Treatment Approach
- Mild to Moderate Rosacea: Topical treatments like metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin are commonly used.
- Moderate to Severe Rosacea: Oral antibiotics, particularly tetracyclines, are often necessary for persistent cases.
Topical Treatments
- Metronidazole: A topical antibiotic that reduces inflammation. Available in cream, gel, or lotion, applied once or twice daily.
- Azelaic Acid: Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial, available in cream, gel, or foam. Applied twice daily.
- Ivermectin: Anti-inflammatory and anti-parasitic, effective for papules and pustules. Applied once daily.
Oral Antibiotics
- Tetracyclines: Commonly used for reducing inflammation and treating papules and pustules. Long-term use of sub-antimicrobial doses of doxycycline is recommended to avoid antibiotic resistance.
Refractory Disease
Oral isotretinoin may be considered for cases that do not respond to standard treatments. This potent medication is effective but requires close monitoring due to potential side effects.
Ocular Manifestations
Rosacea can affect the eyes, leading to dryness, irritation, and inflammation. Treatment includes lid scrubs, warm compresses, and topical or oral antibiotics. In some cases, topical cyclosporine is used to reduce inflammation.
Phymatous Skin Changes
Phymatous changes involve skin thickening, particularly around the nose (rhinophyma). Treatments include laser ablation and surgical procedures to remove excess tissue and reshape the affected area.
Special Cases
- Granulomatous Rosacea: Presents with firm bumps and may require oral antibiotics or treatments like isotretinoin or topical pimecrolimus.
- Paediatric Rosacea: Managed similarly to adults, with topical treatments and oral antibiotics (excluding tetracyclines for children under nine).
- Pyoderma Faciale: A severe form of rosacea, often treated with oral prednisone and isotretinoin.
Conclusion
While rosacea is a chronic condition, it can be managed effectively with a personalised treatment plan. By working closely with a healthcare provider, individuals can control symptoms, enhance skin health, and improve their overall quality of life.
Treatments for Rosacea
Is rosacea causing redness, flushing, and discomfort? Regain control of your skin with Rejuvenate Face's expert-led rosacea treatments. We'll create a tailored plan and help you achieve a more even complexion. Schedule a consultation and take the first step towards clearer, healthier skin.
Rosacea Treatment Guide
Discover expert tips and treatments for rosacea in our comprehensive guide. Learn how to soothe redness and achieve healthier skin - start your journey today!

Skincare for Rosacea
Discover expert tips and gentle products for managing rosacea. Learn how to soothe redness and strengthen your skin barrier—start your journey to calmer skin today!

SkinMed Rosacea Protocol
Transform your skin with the SkinMed® TripleLock® Rosacea Protocol—clinically proven to reduce redness, inflammation, and triggers for long-lasting results. Learn more today!


FAQs About Rosacea: Understanding and Managing the Condition
To help you better understand and manage rosacea, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) that provide detailed insights into this condition
Book NowWhat Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but researchers believe it is due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of rosacea are more likely to develop it. Other potential triggers include:
- Immune system response: Some research suggests that an abnormal reaction of the immune system might play a role in causing the inflammation associated with rosacea.
- Microorganisms: A type of mite called Demodex folliculorum, which lives on the skin, is found in higher numbers on people with rosacea. Bacteria like Helicobacter pylori have also been linked to the condition.
- Blood vessel issues: Blood vessels may dilate more easily in people with rosacea, contributing to flushing and redness.
- Triggers: Factors such as sun exposure, alcohol, spicy foods, stress, and extreme temperatures can exacerbate symptoms but are not direct causes.
What Are the Main Symptoms of Rosacea?
Rosacea symptoms can vary from person to person, but they generally include:
- Facial redness (erythema): Persistent redness usually occurs in the central part of the face, such as the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin.
- Visible blood vessels: Small, visible blood vessels may appear on the skin’s surface, especially on the cheeks and nose.
- Bumps and pimples: Some people develop small, red, pus-filled bumps that resemble acne.
- Skin thickening (phymatous changes): In more advanced cases, the skin may thicken and enlarge, especially around the nose (rhinophyma).
- Eye irritation: Some individuals experience eye problems like dryness, irritation, and swelling, a condition called ocular rosacea.
Recognising these symptoms early on can lead to a more effective management plan and help reduce the risk of progression.
How Is Rosacea Diagnosed?
Rosacea is diagnosed based on a clinical evaluation of your symptoms and medical history. There are no specific tests for rosacea, but a dermatologist will typically look for the characteristic symptoms such as facial redness, bumps, and visible blood vessels. They may ask about potential triggers or flare-ups, as well as your family history of skin conditions. In some cases, the doctor may rule out other conditions, such as lupus or acne, which can present with similar symptoms.
If rosacea affects the eyes, an ophthalmologist may be involved in diagnosing ocular rosacea. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms effectively and preventing the condition from worsening.
What Treatments Are Available for Rosacea?
Although rosacea cannot be cured, several treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Treatment options include:
- Topical medications: These are applied directly to the skin to reduce redness, inflammation, and bumps. Common options include metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin.
- Oral antibiotics: For more severe cases, especially with papules and pustules, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or tetracycline may be prescribed.
- Laser and light therapies: These treatments help reduce visible blood vessels and facial redness by targeting the blood vessels beneath the skin.
- Lifestyle adjustments: It is key to identify and avoid triggers. This includes wearing sunscreen daily, avoiding spicy foods and alcohol, and managing stress.
- Skincare: It is important to follow a gentle skincare routine with non-irritating products. Moisturisers and cleansers designed for sensitive skin can help protect the skin’s barrier.
- Ocular treatment: For ocular rosacea, treatments like lid scrubs, warm compresses, and prescription eye drops may be recommended.


